AWS Api Gateway Authorization(Access Control) with IAM, Cognito or Lambda Authorizer
Learn how to set up control access to your AWS API Gateway endpoints with IAM permissions, Amazon Cognito User Pools or Lambda Authorizer (previously named Custom Authorizer).
Amazon Cognito User Pools
AWS API Gateway Console
-
On Api Gateway console left panel, choose your API and select ‘Authorizers’.

-
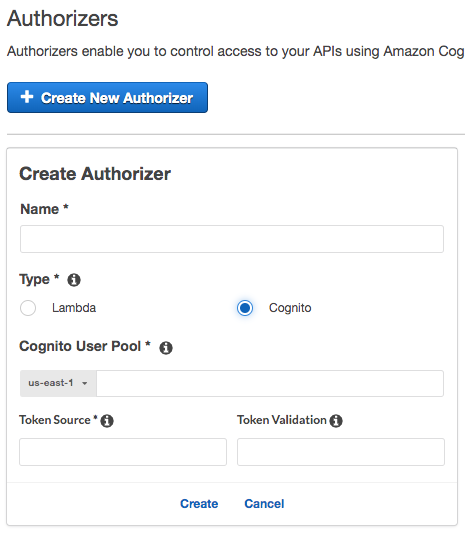
On Authorizers menu, select ‘Create New Authorizer’.
-
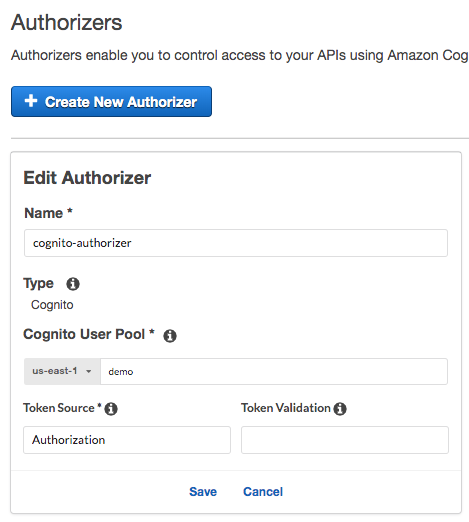
Select ‘Cognito’ and fill up the form with the right information. For Token Source, you use ‘Authorization’ header with default configuration. Save the changes to create a new Cognito Authorizer.
-
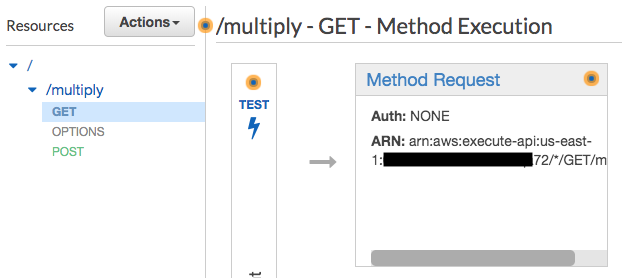
Select ‘Resources’ on the left panel. Select the resource and method that you want to secure.
-
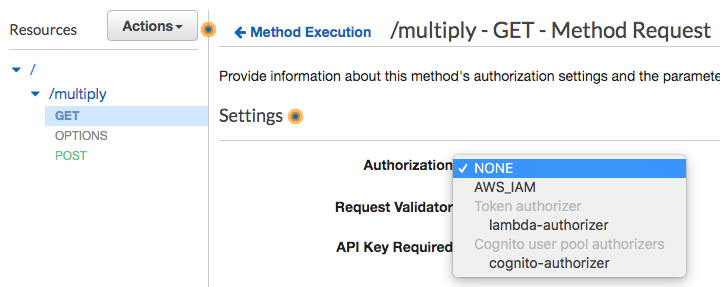
On Method Request menu, in settings section, click pencil icon on the right of Authorization item to open up Authorization option menu.
-
Choose Cognito Authorizer that you created in step 3. Remember to click the check icon appears to the right to save the configuration. There may be a prompt alert that asks for permission.
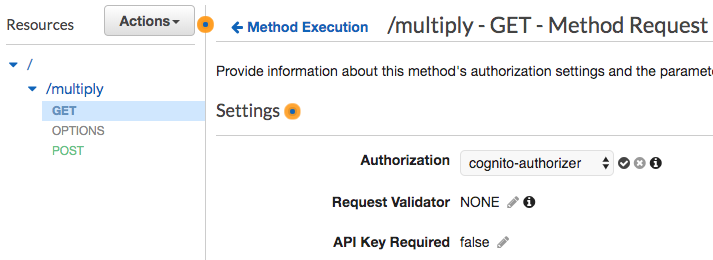
-
When control access is configured and saved, you should deploy your API for it to take effect. Choose the stage that you want to deploy your API to and your API endpoint will be ready to be used.
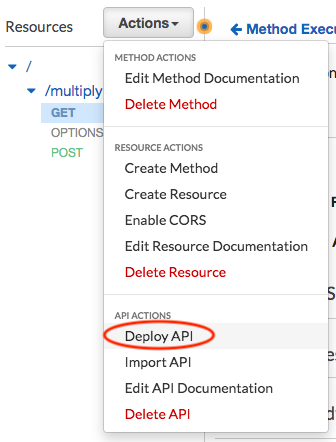
AWS SAM / Swagger with AWS CloudFormation
AWS SAM API Auth Object
You can use AWS SAM API Auth Object to configure your yaml file to use Cognito Authorizer based on the following example. You can refer to AWS SAM documentation for more information.
Note that for AWS::Serverless::Function, if the referred API has a default authorizer set, you can use Auth item to override the default authorizer by setting Authorizer: ‘None’.
MyApi:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
StageName: Prod
Auth:
DefaultAuthorizer: MyCognitoAuth
Authorizers:
MyCognitoAuth:
# Can also accept an array
UserPoolArn: !GetAtt MyCognitoUserPool.Arn
Identity: # OPTIONAL
# OPTIONAL; Default: 'Authorization'
Header: MyAuthorizationHeader
# OPTIONAL
ValidationExpression: myAuthValidationExp
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
FunctionName: MyFunction
...
Events:
Post:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /compute
Method: POST
RestApiId: !Ref MyApi
Auth:
Authorizer: MyCognitoAuth
OpenAPI’s Swagger
You can use OpenAPI’s Swagger object’s Security Definitions object. CloudFormation supports Swagger for API Gateway configuration.
securityDefinitions:
CognitoAuthorizer:
type: "apiKey"
name: "Authorization"
in: "header"
x-amazon-apigateway-authtype: "cognito_user_pools"
x-amazon-apigateway-authorizer:
providerARNs:
# you can also use !GetAtt MyCognitoUserPool.Arn
- "arn:aws:cognito-idp:region:accNum:userpool/poolId"
type: "cognito_user_pools"
Include the above Cognito Authorizer security definition under Definition Body of your AWS::Serverless::API object.
Then, add a security item that points to the securityDefinition under your API path method.
MyApi:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
StageName: Prod
DefinitionBody:
swagger: '2.0'
basePath: '/Prod'
schemes:
- 'https'
securityDefinitions: # 1 Add security definition
CognitoAuthorizer:
type: "apiKey"
name: "Authorization"
in: "header"
x-amazon-apigateway-authtype: "cognito_user_pools"
x-amazon-apigateway-authorizer:
providerARNs:
- # userPool ARN
type: "cognito_user_pools"
paths:
/myMethod:
post:
produces:
- "application/json"
responses:
"200":
description: "200 response"
headers:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Methods:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Headers:
type: "string"
security: # 2 Add security item
- CognitoAuthorizer: []
x-amazon-apigateway-integration:
uri: # api-gateway-arn
responses: {}
httpMethod: "POST"
type: "aws_proxy"
For x-amazon-apigateway-integration uri, you can refer to this AWS SAM example on GitHub.
IAM permissions
AWS API Gateway Console
-
On Api Gateway console left panel, choose your API and select ‘Resources’.

-
On the resource list, select the resource and method that you want to secure.

-
On Method Request menu, in settings section, click pencil icon on the right of Authorization item to open up Authorization option menu.

-
Choose AWS_IAM for authorization. Remember to click the check icon appears to the right to save the configuration. There may be a prompt alert that asks for permission.
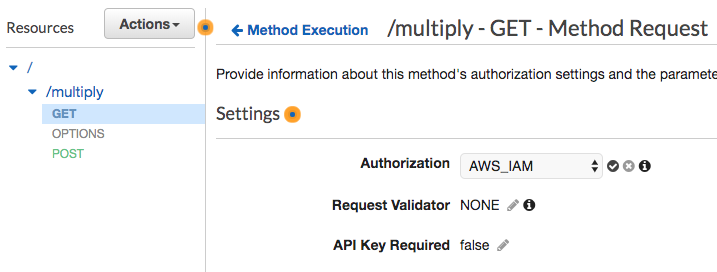
-
When control access is configured and saved, you should deploy your API for it to take effect. Choose the stage that you want to deploy your API to and your API endpoint will be ready to be used.

AWS SAM / Swagger with AWS CloudFormation
AWS SAM API Auth Object
With AWS SAM v1.11.0, AWS SAM supports IAM Authorizer.
You can use AWS SAM API Auth Object to configure your yaml file to use IAM Authorizer based on the following example.
Note that for AWS::Serverless::Function, if the referred API has a default authorizer set, you can use Auth item to override the default authorizer by setting Authorizer: ‘None’.
MyApi:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
StageName: Prod
Auth:
DefaultAuthorizer: AWS_IAM
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
FunctionName: MyFunction
...
Events:
Post:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /compute
Method: POST
RestApiId: !Ref MyApi
Auth:
Authorizer: AWS_IAM
With AWS SAM v1.10.0, authorization via AWS IAM is not supported yet. Earlier in January 2019, there was RFC: API Gateway IAM (AWS_IAM) Authorizers.
Thanks to Takahiro Horike that completed a pull request for adding AWS IAM authorizer. When it is released, you will be able to use it like this based on the pull request document.
OpenAPI’s Swagger
You can use OpenAPI’s Swagger object’s Security Definitions object. CloudFormation supports Swagger for API Gateway configuration.
securityDefinitions:
AwsIamAuthorizer:
type: "apiKey"
name: "Authorization"
in: "header"
x-amazon-apigateway-authtype: "awsSigv4"
Include the above AWS IAM Authorizer security definition under Definition Body of your AWS::Serverless::API object.
Then, add a security item that points to the securityDefinition under your API path method.
MyApi:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
StageName: Prod
DefinitionBody:
swagger: '2.0'
basePath: '/Prod'
schemes:
- 'https'
securityDefinitions: # 1 Add security definition
AwsIamAuthorizer:
type: "apiKey"
name: "Authorization"
in: "header"
x-amazon-apigateway-authtype: "awsSigv4"
paths:
/myMethod:
post:
produces:
- "application/json"
responses:
"200":
description: "200 response"
headers:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Methods:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Headers:
type: "string"
security: # 2 Add security item
- AwsIamAuthorizer: []
x-amazon-apigateway-integration:
uri: # api-gateway-arn
responses: {}
httpMethod: "POST"
type: "aws_proxy"
For x-amazon-apigateway-integration uri, you can refer to this AWS SAM example on GitHub.
Custom Authorizer
AWS API Gateway Console
-
On Api Gateway console left panel, choose your API and select ‘Authorizers’.

-
On Authorizers menu, select ‘Create New Authorizer’.
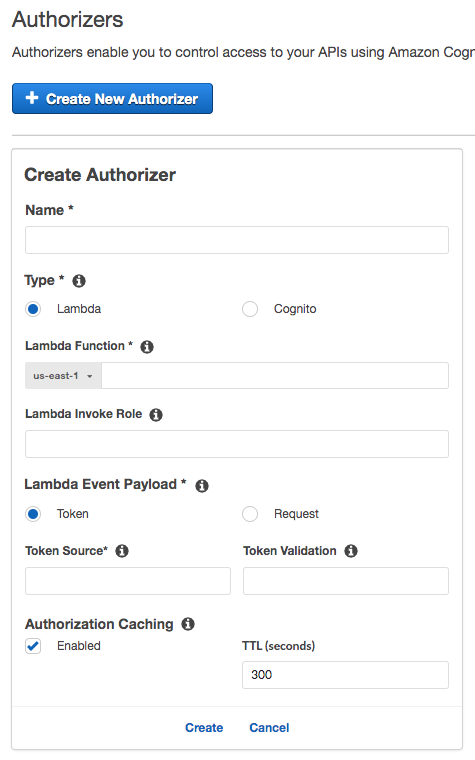
-
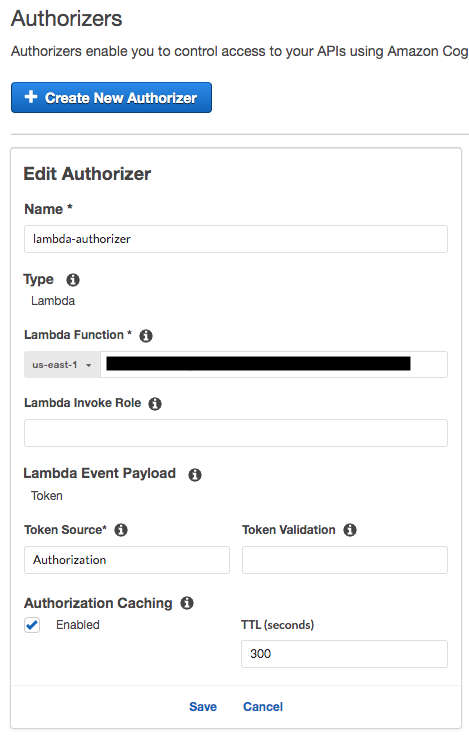
Select ‘Lambda’ and fill up the form with the intended configuration.
Choose your lambda authorizer function.
For Lambda Invoke Role, you can check out AWS Security Token Service.
For Token Source, you use ‘Authorization’ header with default configuration.
Save the changes to create a new Lambda Authorizer.
-
Select ‘Resources’ on the left panel. Select the resource and method that you want to secure.

-
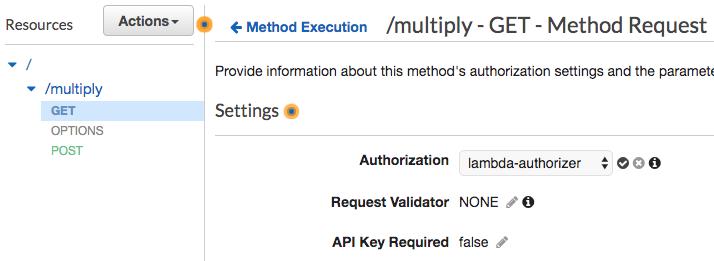
On Method Request menu, in settings section, click pencil icon on the right of Authorization item to open up Authorization option menu.

-
Choose Lambda Authorizer that you created in step 3. Remember to click the check icon appears to the right to save the configuration. There may be a prompt alert that asks for permission.
-
When control access is configured and saved, you should deploy your API for it to take effect. Choose the stage that you want to deploy your API to and your API endpoint will be ready to be used.

AWS SAM / Swagger with AWS CloudFormation
AWS SAM API Auth Object
You can use AWS SAM API Auth Object to configure your yaml file to use Lambda Authorizer based on the following example. MyAuthFunction refers to your Lambda Authorizer function.
Note that for AWS::Serverless::Function, if the referred API has a default authorizer set, you can use Auth item to override the default authorizer by setting Authorizer: ‘None’.
MyApi:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
StageName: Prod
Auth:
DefaultAuthorizer: MyLambdaTokenAuth # OPTIONAL
Authorizers:
MyLambdaTokenAuth:
FunctionPayloadType: TOKEN
FunctionArn: !GetAtt MyAuthFunction.Arn
FunctionInvokeRole: arnOfRole
Identity:
Header: 'Authorization'
ValidationExpression: customExpr # OPTIONAL
# Default ReauthorizeEvery: 300 seconds
ReauthorizeEvery: 20 # OPTIONAL;
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
FunctionName: MyFunction
...
Events:
Post:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /compute
Method: POST
RestApiId: !Ref MyApi
Auth:
Authorizer: MyLambdaTokenAuth
Another example:
MyApi:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
StageName: Prod
Auth:
DefaultAuthorizer: MyLambdaRequestAuthorizer
Authorizers:
MyLambdaRequestAuthorizer:
FunctionPayloadType: REQUEST
FunctionArn: !GetAtt MyAuthFunction.Arn
# FunctionInvokeRole: !Ref MyRole
Identity:
# Must specify at least one of
# Headers, QueryStrings,
# StageVariables, or Context
QueryStrings:
- auth
# NOTE: Additional options:
# Headers:
# - Authorization
# StageVariables:
# - AUTHORIZATION
# Context:
# - authorization
# Default ReauthorizeEvery: 300 seconds
# ReauthorizeEvery: 100 # OPTIONAL;
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
FunctionName: MyFunction
...
Events:
Post:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /compute
Method: POST
RestApiId: !Ref MyApi
Auth:
Authorizer: MyLambdaRequestAuthorizer
You can refer this AWS SAM github example for more information.
OpenAPI’s Swagger
You can use OpenAPI’s Swagger object’s Security Definitions object. CloudFormation supports Swagger for API Gateway configuration.
securityDefinitions:
LambdaAuthorizer:
type: "apiKey"
name : "Authorization"
in: "header"
x-amazon-apigateway-authtype: "oauth2"
x-amazon-apigateway-authorizer:
authorizerUri:
- # ARN of Lambda Authorizer
type: "token"
authorizerCredentials: "arn:aws:iam::account-id:role"
identityValidationExpression: "^x-[a-z]+"
authorizerResultTtlInSeconds: 60
Your authorizerUri is the ARN of your Lambda function. It is in this format:
arn:aws:apigateway:us-east-1:lambda:path/2015-03-31/functions/arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:account-id:function:function-name/invocations.
Include the above Lambda Authorizer security definition under Definition Body of your AWS::Serverless::API object.
Then, add a security item that points to the securityDefinition under your API path method.
MyApi:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Api
Properties:
StageName: Prod
DefinitionBody:
swagger: '2.0'
basePath: '/Prod'
schemes:
- 'https'
securityDefinitions: # 1 Add security definition
LambdaAuthorizer:
type: "apiKey"
name : "Authorization"
in: "header"
x-amazon-apigateway-authtype: "oauth2"
x-amazon-apigateway-authorizer:
authorizerUri:
- # ARN of Lambda Authorizer
type: "token"
authorizerCredentials: "arn:aws:iam::acc-id:role"
identityValidationExpression: "^x-[a-z]+"
authorizerResultTtlInSeconds: 60
paths:
/myMethod:
post:
produces:
- "application/json"
responses:
"200":
description: "200 response"
headers:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Methods:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Headers:
type: "string"
security: # 2 Add security item
- LambdaAuthorizer: []
x-amazon-apigateway-integration:
uri: # api-gateway-arn
responses: {}
httpMethod: "POST"
type: "aws_proxy"
For x-amazon-apigateway-integration uri, you can refer to this AWS SAM example on GitHub.
Summary
In conclusion, it is important to secure your AWS API Gateway endpoints to prevent them to be misused by third parties which will incur unnecessary cost to you. With this, hopefully, you can set up authorization or control access to your AWS API Gateway endpoints.
Support Jun
Thank you for reading! 
If you are preparing for Software Engineer interviews, I suggest Elements of Programming Interviews in Java for algorithm practice. Good luck!
You can also support me by following me on Medium or Twitter.
Feel free to contact me if you have any questions.



Comments