Create AWS Lambda Layers Using AWS SAM
Learn how to create a Lambda Layer using AWS SAM (Serverless Application Model) and CloudFormation in YAML to reuse code, write zero redundant code and reduce Lambda deployment size.
AWS Lambda Layers
Lambda Layers can be thought of as additional code added on top of a Lambda function. A Lambda Layer is a ZIP archive / file that contains code and can be imported by Lambda functions.
In other words, you can extract and reuse common code by keeping the code in a Lambda Layer and attach it to multiple Lambda functions.
As for limit, a Lambda function can only use up to 5 layers at a time. And, the total size of unzipped code of Lambda plus the attached Layers cannot exceed 250MB.
You can create your own layers, or use layers published by AWS and other AWS customers.
AWS CloudFormation
You can create a Lambda Layer using AWS::Lambda::LayerVersion entity by setting its content to point to a ZIP archive containing your code stored in an S3 bucket.
To keep older versions of your Lambda Layer, set your Lambda LayerVersion UpdateReplacePolicy and DeletionPolicy attribute value as Retain.
AWS::Lambda::LayerVersion example:
MyLayer:
Type: "AWS::Lambda::LayerVersion"
UpdateReplacePolicy: Retain
DeletionPolicy: Retain
Properties:
CompatibleRuntimes:
- python3.6
- python3.7
- python3.8
Content:
S3Bucket: my-bucket-us-west-2-123456789012
S3Key: layer.zip
Description: My layer
LayerName: my-layer
LicenseInfo: MIT
AWS SAM
AWS SAM provides a simpler syntax via AWS::Serverless::LayerVersion and additional function that allows us that help us package and deploy local code.
When you develop your Lambda Layer, you can write your code in a file relative to SAM template by setting LayerVersion ContentUri property to point to a relative local path.
For example, if your code is inside myFolder, set ContentUri as ContentUri: ./myFolder.
AWS::Serverless::LayerVersion example:
Resources:
AwsServices:
Type: AWS::Serverless::LayerVersion
Properties:
LayerName: my-layer
Description: My layer
ContentUri: ./myLayer
CompatibleRuntimes:
- python3.6
- python3.7
- python3.8
LicenseInfo: MIT
RetentionPolicy: Retain
Lambda Layers Project Structure
Lambda Layers ZIP archives are extracted to /opt folder in a Lambda function execution environment. Each language runtime looks for libraries in a different location in /opt folder.
In other words, you should place your code within the required folder path - the folder path supported by the function runtime. Refer to AWS document for more detailed information.
I tried Lambda Layers in Python and it seems that code placed within python folder would be import-able in a Lambda Function at Python runtime 3.X. If you want to limit your Lambda Layer to a specific runtime, let’s say Python3.8, then you can put it in python/lib/python3.8/site-packages folder.
For Python example, if your LayerVersion ContentUri is ./myLayer, you need to create a folder named python and put your Python files within ./myLayer/python folder.
In the Lambda Function that imports this Layer via import file1, you can print to see the location of your imported file from Layer. The output is <module 'file1' from '/opt/python/file1.py'> as expected.
Lambda Layer Folder structure example:
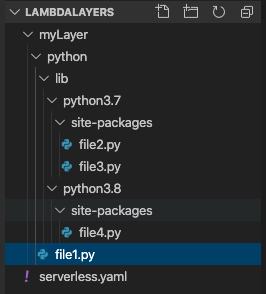
The following is the list the folders specifed on AWS Lambda Layers document. Node.js
- nodejs/node_modules
- nodejs/node8/node_modules (NODE_PATH)
Python
- python
- python/lib/python3.8/site-packages
Java
- java/lib (classpath)
Ruby
– ruby/gems/2.5.0 (GEM_PATH)
- ruby/lib (RUBY_LIB)
All
– bin (PATH)
- lib (LD_LIBRARY_PATH)
CloudFormation Role Permission
To enable CloudFormation to create Lambda Layers for you, the assumed role needs to have permission to access and manipulate AWS Lambda Layers. You can attach the following inline policies to your CloudFormation role in order for it to create Lambda Layers for you.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:GetLayerVersion",
"lambda:PublishLayerVersion",
"lambda:DeleteLayerVersion",
"lambda:ListLayerVersions",
"lambda:ListLayers",
"lambda:AddLayerVersionPermission",
"lambda:RemoveLayerVersionPermission"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Caveat
There is no Lambda Layer alias that points to a specific version of a Lambda Layer. Thus, Lambda functions that uses a layer has to be updated to use the latest version of Layer. It is good that it won’t automatically use new code from new Layer version that may potentially break existing Lambda functionality.
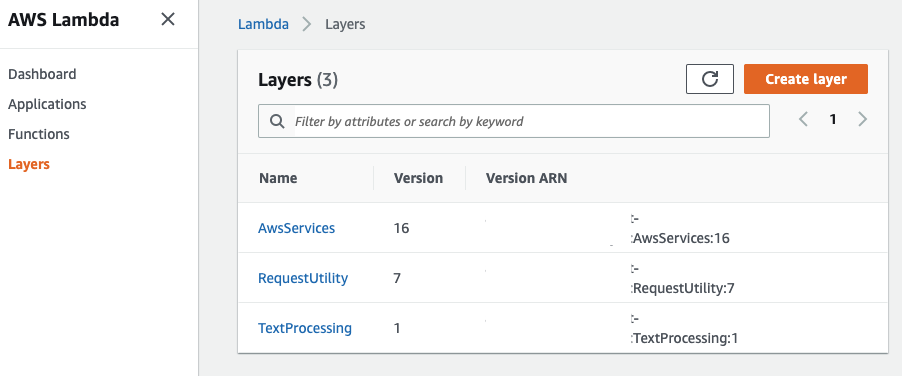
Lambda Layers On AWS Console
To verify Lambda Layers are actually created, you can use AWS CLI or go to AWS Console (Lambda) to see your Lambda Layers.
Add to Lambda Function
You can read Attach AWS Lambda Layers to Lambda Functions article to learn how to add a Lambda Layer to a Lambda function.
Support Jun
Thank you for reading! 
If you are preparing for Software Engineer interviews, I suggest Elements of Programming Interviews in Java for algorithm practice. Good luck!
You can also support me by following me on Medium or Twitter.
Feel free to contact me if you have any questions.




Comments